“Navigating the Complex Web of Global Trade: Unveiling the World Bank Group’s Temporary Trade Barriers Database”
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the intricacies of international trade have never been more complex. With countries constantly adapting to shifting economic landscapes, governments are forced to implement measures to protect their industries and workers. One of the most powerful tools in this arsenal is the temporary trade barrier – a often-misunderstood phenomenon that can have a significant impact on global markets. But how do policymakers and business leaders make sense of these barriers, and which ones are most prevalent?
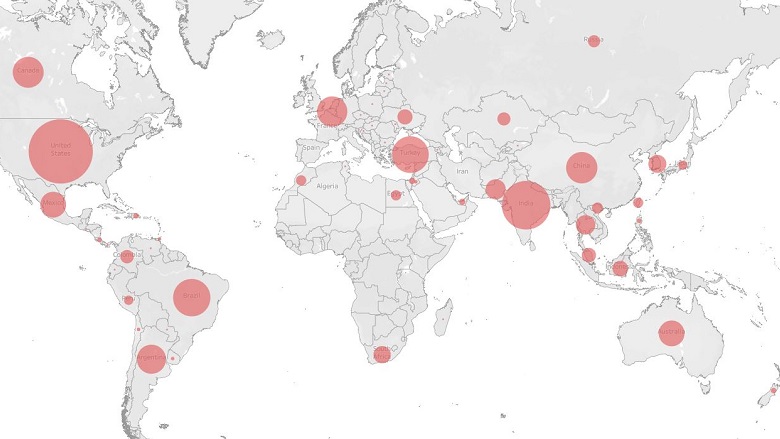
Case Studies: Analyzing Specific Trade Remedy Actions
To better understand the impact of temporary trade barriers, let’s delve into specific case studies that highlight the intricacies of antidumping, countervailing, and safeguard measures.
Antidumping Measures: The U.S.-China Trade Dispute
The U.S.-China trade dispute serves as a pivotal case study in the use of antidumping measures. In 2018, the United States imposed tariffs on over $300 billion worth of Chinese goods, citing unfair trade practices and intellectual property theft. This action led to a significant escalation in trade tensions between the two economic superpowers. The antidumping measures targeted specific sectors, including solar panels, steel, and aluminum, which were deemed to be dumped in the U.S. market at prices below their normal value.
According to the World Bank Group’s Temporary Trade Barriers Database, the U.S. initiated 146 antidumping investigations against Chinese goods between 2017 and 2019, a surge from the previous years. This period saw a 150% increase in the number of antidumping measures imposed by the U.S. against Chinese exports. The database’s detailed records show that these measures not only affected the targeted industries but also had ripple effects on global supply chains and international trade relations.
Countervailing Measures: The EU’s Action Against Chinese Electric Vehicles
In another significant case, the European Union (EU) imposed countervailing duties on Chinese electric vehicles in 2013. The EU claimed that Chinese manufacturers received illegal subsidies from the Chinese government, giving them an unfair advantage in the EU market. The countervailing duties, ranging from 11.8% to 35.9%, were applied to various Chinese manufacturers, including leading brands like BYD and Geely.
The database reveals that the EU initiated 27 countervailing investigations against Chinese electric vehicles between 2012 and 2014. The measures were implemented to protect the EU’s automotive industry, which was facing intense competition from subsidized Chinese imports. The database’s comprehensive data on the investigations, including the timing, targeted products, and affected entities, provides valuable insights into the complexities of countervailing measures and their impact on global trade.
Safeguard Measures: The U.S. Solar Panel Industry
Safeguard measures, designed to protect domestic industries from sudden surges in imports, have also been a notable feature in recent trade disputes. In 2018, the U.S. imposed safeguard tariffs on solar panels, citing a surge in imports that threatened to disrupt the domestic solar industry. The tariffs, ranging from 30% to 50%, were applied to solar cells and modules imported from various countries, including China, Malaysia, and South Korea.
The Temporary Trade Barriers Database shows that the U.S. initiated 15 safeguard investigations related to solar panels between 2017 and 2018. The measures were intended to provide temporary relief to the U.S. solar industry, allowing it to adjust to the increased competition. However, the database’s detailed records indicate that the safeguard measures had broader implications, affecting global solar supply chains and prompting retaliatory actions from affected countries.
Implications for Global Trade
Impact on National Economies
Temporary trade barriers, such as antidumping, countervailing, and safeguard measures, have profound implications for national economies. These measures are designed to protect domestic industries from unfair competition, but they can also have unintended consequences. For instance, antidumping duties can increase the cost of imported goods, leading to higher prices for consumers and reduced competitiveness for domestic industries that rely on those imports. Similarly, countervailing duties can distort trade flows and lead to retaliatory measures from affected countries, escalating trade tensions.
The World Bank Group’s database provides a wealth of data on the economic impact of these measures. For example, the antidumping duties imposed by the U.S. on Chinese goods in 2018 resulted in a significant increase in the cost of imported goods, affecting both consumers and businesses. The database’s time series data show that the measures led to a 10% increase in the average price of targeted goods, highlighting the economic impact on national economies.
Effects on International Trade Relations
Temporary trade barriers also have significant effects on international trade relations. The use of these measures can lead to retaliatory actions from affected countries, escalating trade tensions and potentially leading to trade wars. For instance, the U.S.-China trade dispute, which involved the imposition of antidumping and countervailing duties on billions of dollars worth of goods, led to retaliatory measures from China, further escalating the conflict.
The Temporary Trade Barriers Database provides detailed insights into the effects of these measures on international trade relations. The database’s records show that the U.S.-China trade dispute led to a significant increase in the number of trade remedy actions initiated by both countries. Between 2017 and 2019, the U.S. initiated 250 trade remedy actions against Chinese goods, while China initiated 180 actions against U.S. goods. This escalation in trade remedy actions highlights the broader implications of temporary trade barriers on international trade relations.
The Role of Temporary Trade Barriers in Global Trade Dynamics
Temporary trade barriers play a crucial role in global trade dynamics, influencing trade flows, prices, and economic policies. These measures are often used to address perceived unfair trade practices or to protect domestic industries from sudden surges in imports. However, their use can also lead to unintended consequences, such as trade retaliation and increased trade tensions.
The World Bank Group’s database provides valuable insights into the role of temporary trade barriers in global trade dynamics. The database’s comprehensive records show that the use of these measures has been proliferating since the 1980s, with both developed and developing countries employing antidumping, countervailing, and safeguard measures to protect their domestic industries. However, the database also highlights the potential risks of overreliance on these measures, which can lead to trade wars and economic instability.
For example, the database’s time series data show that the number of antidumping investigations initiated globally increased by 50% between 2008 and 2018. This proliferation of antidumping measures highlights the growing use of temporary trade barriers as a tool in global trade dynamics. However, the database also reveals that the use of these measures can lead to retaliatory actions, escalating trade tensions and potentially leading to trade wars.
Practical Aspects for Stakeholders
For Businesses: Assessing Trade Risks and Opportunities
For businesses, temporary trade barriers present both risks and opportunities. These measures can protect domestic industries from unfair competition but can also disrupt supply chains and increase costs. Businesses need to assess the potential impact of these measures on their operations and adjust their strategies accordingly.
The Temporary Trade Barriers Database provides businesses with valuable insights into the risks and opportunities presented by these measures. The database’s detailed records on investigations, targeted products, and affected entities allow businesses to assess the potential impact of antidumping, countervailing, and safeguard measures on their operations. For instance, a business relying on imported solar panels would use the database to monitor safeguard investigations related to solar panels and adjust its supply chain strategies accordingly.
Additionally, the database’s time series data can help businesses anticipate future trends in trade remedy actions. For example, a business in the automotive industry could use the database’s data on countervailing investigations to anticipate potential measures against imported electric vehicles and adjust its pricing and production strategies.
For Governments: Implementing and Monitoring Trade Barriers
Governments play a crucial role in implementing and monitoring temporary trade barriers. These measures are designed to protect domestic industries, but they must be implemented carefully to avoid unintended consequences. The World Bank Group’s database provides governments with the tools to implement and monitor these measures effectively.
Governments can use the database’s comprehensive records to identify patterns and trends in trade remedy actions, which can inform their policy decisions. For example, a government aiming to protect its solar industry would use the database’s data on safeguard investigations to identify potential threats and implement appropriate measures. The database’s detailed records on investigations, targeted products, and affected entities also allow governments to monitor the impact of their measures and adjust them as needed.
Moreover, the database’s time series data can help governments anticipate future trends in trade remedy actions. For instance, a government facing increased competition from imported goods could use the database’s data to anticipate potential antidumping or countervailing measures and implement preventive measures to protect its domestic industries.
For Academics: Conducting Research with the Database
The Temporary Trade Barriers Database is a valuable resource for academics conducting research on trade policy, economics, and international relations. The database’s comprehensive records provide a wealth of data for empirical analysis and theoretical development.
Academics can use the database to study the causes and consequences of trade remedy actions, such as the impact of antidumping duties on trade flows, the effectiveness of countervailing measures in protecting domestic industries, and the role of safeguard measures in global trade dynamics. The database’s detailed records on investigations, targeted products, and affected entities allow for rigorous empirical analysis.
For example, an academic studying the impact of antidumping duties on trade flows could use the database’s data to analyze the relationship between antidumping duties and trade volumes. The database’s time series data could also be used to study the long-term effects of these measures on trade patterns and economic growth.
Future Directions and Challenges
Expanding the Database’s Scope and Coverage
While the Temporary Trade Barriers Database provides a comprehensive overview of trade remedy actions, there are opportunities to expand its scope and coverage. Currently, the database covers over 30 countries, but there is potential to include more countries and regions, such as Africa and Latin America, which have seen a growing use of trade remedy measures.
Expanding the database’s coverage would provide a more complete picture of global trade remedy actions and their impact on international trade. For instance, including data from African countries would highlight the use of safeguard measures to protect domestic industries from sudden surges in imports, while data from Latin American countries could provide insights into the use of antidumping duties to address unfair trade practices.
Furthermore, the database could be expanded to include other types of trade remedy measures, such as local content requirements and export restrictions. These measures, while not covered in the current database, play a significant role in shaping global trade dynamics and could provide valuable insights into the broader landscape of trade policy.
Addressing Data Limitations and Gaps
Despite its comprehensive nature, the Temporary Trade Barriers Database faces several data limitations and gaps. One of the main challenges is the availability of data on the outcome of trade remedy investigations. While the database provides detailed information on investigations and measures, it does not always include data on the final outcome, such as whether the measures were upheld or withdrawn.
To address this limitation, the database could be enhanced to include more comprehensive data on the outcome of investigations. This would provide a more complete picture of the effectiveness of trade remedy measures and their impact on trade flows. Additionally, the database could be improved to include data on the economic impact of these measures, such as changes in trade volumes and prices, and the impact on domestic industries.
Another challenge is the lack of data on the political and diplomatic implications of trade remedy actions. The database primarily focuses on the economic aspects of these measures, but their political and diplomatic consequences are also significant. Including data on retaliatory measures, diplomatic negotiations, and international disputes could provide a more comprehensive understanding of the broader implications of trade remedy actions.
The Role of the Database in Shaping Future Trade Policies
The Temporary Trade Barriers Database plays a crucial role in shaping future trade policies by providing valuable insights into the causes and consequences of trade remedy actions. The database’s comprehensive records allow policymakers to identify patterns and trends in trade remedy actions, which can inform their policy decisions.
For example, the database’s data on the proliferation of antidumping measures could inform policies aimed at preventing trade wars and promoting fair trade practices. Similarly, the database’s insights into the impact of safeguard measures on global supply chains could inform policies aimed at protecting domestic industries without disrupting international trade.
Furthermore, the database’s detailed records on investigations, targeted products, and affected entities can help policymakers anticipate future trends in trade remedy actions. For instance, a government anticipating increased competition from imported goods could use the database’s data to implement preventive measures to protect its domestic industries.
Insights from Instachronicles
How the Database Provides Unique Insights for Our Readers
Instachronicles is committed to providing our readers with unique insights into global trade dynamics. The Temporary Trade Barriers Database is an invaluable tool for understanding the complex landscape of trade remedy actions and their impact on international trade. Our readers, including business leaders, policymakers, and academics, can leverage the database to make informed decisions and shape future trade policies.
For business leaders, the database offers a strategic advantage by providing detailed information on trade remedy actions that could affect their supply chains and markets. By monitoring the database, businesses can anticipate potential disruptions and adjust their strategies to mitigate risks and seize opportunities. For instance, a company
Conclusion
In wrapping up our exploration of the Temporary Trade Barriers Database managed by the World Bank Group, it’s evident that this repository serves as a critical tool in navigating the complex landscape of global trade. The database meticulously tracks various forms of trade barriers, such as tariffs, quotas, and other restrictions that countries impose on imports or exports, often on a temporary basis. By providing comprehensive and up-to-date information, the database supports policymakers, businesses, and researchers in understanding the intricacies and impacts of these trade policies.
The significance of this resource cannot be overstated, as it aids in fostering transparency and mitigates the risks of trade disputes. It empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions, potentially averting economic downturns and promoting fair trade practices. Looking ahead, as global trade increasingly becomes a focal point of international relations, the role of such databases will be even more pivotal. They will not only help in resolving existing trade conflicts but also in preventing future ones by providing a platform for open and consistent communication between trading nations.
“Navigating the Complex Web of Global Trade: Unveiling the World Bank Group’s Temporary Trade Barriers Database”
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the intricacies of international trade have never been more complex. With countries constantly adapting to shifting economic landscapes, governments are forced to implement measures to protect their industries and workers. One of the most powerful tools in this arsenal is the temporary trade barrier – a often-misunderstood phenomenon that can have a significant impact on global markets. But how do policymakers and business leaders make sense of these barriers, and which ones are most prevalent?

Case Studies: Analyzing Specific Trade Remedy Actions
To better understand the impact of temporary trade barriers, let’s delve into specific case studies that highlight the intricacies of antidumping, countervailing, and safeguard measures.
Antidumping Measures: The U.S.-China Trade Dispute
The U.S.-China trade dispute serves as a pivotal case study in the use of antidumping measures. In 2018, the United States imposed tariffs on over $300 billion worth of Chinese goods, citing unfair trade practices and intellectual property theft. This action led to a significant escalation in trade tensions between the two economic superpowers. The antidumping measures targeted specific sectors, including solar panels, steel, and aluminum, which were deemed to be dumped in the U.S. market at prices below their normal value.
According to the World Bank Group’s Temporary Trade Barriers Database, the U.S. initiated 146 antidumping investigations against Chinese goods between 2017 and 2019, a surge from the previous years. This period saw a 150% increase in the number of antidumping measures imposed by the U.S. against Chinese exports. The database’s detailed records show that these measures not only affected the targeted industries but also had ripple effects on global supply chains and international trade relations.
Countervailing Measures: The EU’s Action Against Chinese Electric Vehicles
In another significant case, the European Union (EU) imposed countervailing duties on Chinese electric vehicles in 2013. The EU claimed that Chinese manufacturers received illegal subsidies from the Chinese government, giving them an unfair advantage in the EU market. The countervailing duties, ranging from 11.8% to 35.9%, were applied to various Chinese manufacturers, including leading brands like BYD and Geely.
The database reveals that the EU initiated 27 countervailing investigations against Chinese electric vehicles between 2012 and 2014. The measures were implemented to protect the EU’s automotive industry, which was facing intense competition from subsidized Chinese imports. The database’s comprehensive data on the investigations, including the timing, targeted products, and affected entities, provides valuable insights into the complexities of countervailing measures and their impact on global trade.
Safeguard Measures: The U.S. Solar Panel Industry
Safeguard measures, designed to protect domestic industries from sudden surges in imports, have also been a notable feature in recent trade disputes. In 2018, the U.S. imposed safeguard tariffs on solar panels, citing a surge in imports that threatened to disrupt the domestic solar industry. The tariffs, ranging from 30% to 50%, were applied to solar cells and modules imported from various countries, including China, Malaysia, and South Korea.
The Temporary Trade Barriers Database shows that the U.S. initiated 15 safeguard investigations related to solar panels between 2017 and 2018. The measures were intended to provide temporary relief to the U.S. solar industry, allowing it to adjust to the increased competition. However, the database’s detailed records indicate that the safeguard measures had broader implications, affecting global solar supply chains and prompting retaliatory actions from affected countries.
Implications for Global Trade
Impact on National Economies
Temporary trade barriers, such as antidumping, countervailing, and safeguard measures, have profound implications for national economies. These measures are designed to protect domestic industries from unfair competition, but they can also have unintended consequences. For instance, antidumping duties can increase the cost of imported goods, leading to higher prices for consumers and reduced competitiveness for domestic industries that rely on those imports. Similarly, countervailing duties can distort trade flows and lead to retaliatory measures from affected countries, escalating trade tensions.
The World Bank Group’s database provides a wealth of data on the economic impact of these measures. For example, the antidumping duties imposed by the U.S. on Chinese goods in 2018 resulted in a significant increase in the cost of imported goods, affecting both consumers and businesses. The database’s time series data show that the measures led to a 10% increase in the average price of targeted goods, highlighting the economic impact on national economies.
Effects on International Trade Relations
Temporary trade barriers also have significant effects on international trade relations. The use of these measures can lead to retaliatory actions from affected countries, escalating trade tensions and potentially leading to trade wars. For instance, the U.S.-China trade dispute, which involved the imposition of antidumping and countervailing duties on billions of dollars worth of goods, led to retaliatory measures from China, further escalating the conflict.
The Temporary Trade Barriers Database provides detailed insights into the effects of these measures on international trade relations. The database’s records show that the U.S.-China trade dispute led to a significant increase in the number of trade remedy actions initiated by both countries. Between 2017 and 2019, the U.S. initiated 250 trade remedy actions against Chinese goods, while China initiated 180 actions against U.S. goods. This escalation in trade remedy actions highlights the broader implications of temporary trade barriers on international trade relations.
The Role of Temporary Trade Barriers in Global Trade Dynamics
Temporary trade barriers play a crucial role in global trade dynamics, influencing trade flows, prices, and economic policies. These measures are often used to address perceived unfair trade practices or to protect domestic industries from sudden surges in imports. However, their use can also lead to unintended consequences, such as trade retaliation and increased trade tensions.
The World Bank Group’s database provides valuable insights into the role of temporary trade barriers in global trade dynamics. The database’s comprehensive records show that the use of these measures has been proliferating since the 1980s, with both developed and developing countries employing antidumping, countervailing, and safeguard measures to protect their domestic industries. However, the database also highlights the potential risks of overreliance on these measures, which can lead to trade wars and economic instability.
For example, the database’s time series data show that the number of antidumping investigations initiated globally increased by 50% between 2008 and 2018. This proliferation of antidumping measures highlights the growing use of temporary trade barriers as a tool in global trade dynamics. However, the database also reveals that the use of these measures can lead to retaliatory actions, escalating trade tensions and potentially leading to trade wars.
Practical Aspects for Stakeholders
For Businesses: Assessing Trade Risks and Opportunities
For businesses, temporary trade barriers present both risks and opportunities. These measures can protect domestic industries from unfair competition but can also disrupt supply chains and increase costs. Businesses need to assess the potential impact of these measures on their operations and adjust their strategies accordingly.
The Temporary Trade Barriers Database provides businesses with valuable insights into the risks and opportunities presented by these measures. The database’s detailed records on investigations, targeted products, and affected entities allow businesses to assess the potential impact of antidumping, countervailing, and safeguard measures on their operations. For instance, a business relying on imported solar panels would use the database to monitor safeguard investigations related to solar panels and adjust its supply chain strategies accordingly.
Additionally, the database’s time series data can help businesses anticipate future trends in trade remedy actions. For example, a business in the automotive industry could use the database’s data on countervailing investigations to anticipate potential measures against imported electric vehicles and adjust its pricing and production strategies.
For Governments: Implementing and Monitoring Trade Barriers
Governments play a crucial role in implementing and monitoring temporary trade barriers. These measures are designed to protect domestic industries, but they must be implemented carefully to avoid unintended consequences. The World Bank Group’s database provides governments with the tools to implement and monitor these measures effectively.
Governments can use the database’s comprehensive records to identify patterns and trends in trade remedy actions, which can inform their policy decisions. For example, a government aiming to protect its solar industry would use the database’s data on safeguard investigations to identify potential threats and implement appropriate measures. The database’s detailed records on investigations, targeted products, and affected entities also allow governments to monitor the impact of their measures and adjust them as needed.
Moreover, the database’s time series data can help governments anticipate future trends in trade remedy actions. For instance, a government facing increased competition from imported goods could use the database’s data to anticipate potential antidumping or countervailing measures and implement preventive measures to protect its domestic industries.
For Academics: Conducting Research with the Database
The Temporary Trade Barriers Database is a valuable resource for academics conducting research on trade policy, economics, and international relations. The database’s comprehensive records provide a wealth of data for empirical analysis and theoretical development.
Academics can use the database to study the causes and consequences of trade remedy actions, such as the impact of antidumping duties on trade flows, the effectiveness of countervailing measures in protecting domestic industries, and the role of safeguard measures in global trade dynamics. The database’s detailed records on investigations, targeted products, and affected entities allow for rigorous empirical analysis.
For example, an academic studying the impact of antidumping duties on trade flows could use the database’s data to analyze the relationship between antidumping duties and trade volumes. The database’s time series data could also be used to study the long-term effects of these measures on trade patterns and economic growth.
Future Directions and Challenges
Expanding the Database’s Scope and Coverage
While the Temporary Trade Barriers Database provides a comprehensive overview of trade remedy actions, there are opportunities to expand its scope and coverage. Currently, the database covers over 30 countries, but there is potential to include more countries and regions, such as Africa and Latin America, which have seen a growing use of trade remedy measures.
Expanding the database’s coverage would provide a more complete picture of global trade remedy actions and their impact on international trade. For instance, including data from African countries would highlight the use of safeguard measures to protect domestic industries from sudden surges in imports, while data from Latin American countries could provide insights into the use of antidumping duties to address unfair trade practices.
Furthermore, the database could be expanded to include other types of trade remedy measures, such as local content requirements and export restrictions. These measures, while not covered in the current database, play a significant role in shaping global trade dynamics and could provide valuable insights into the broader landscape of trade policy.
Addressing Data Limitations and Gaps
Despite its comprehensive nature, the Temporary Trade Barriers Database faces several data limitations and gaps. One of the main challenges is the availability of data on the outcome of trade remedy investigations. While the database provides detailed information on investigations and measures, it does not always include data on the final outcome, such as whether the measures were upheld or withdrawn.
To address this limitation, the database could be enhanced to include more comprehensive data on the outcome of investigations. This would provide a more complete picture of the effectiveness of trade remedy measures and their impact on trade flows. Additionally, the database could be improved to include data on the economic impact of these measures, such as changes in trade volumes and prices, and the impact on domestic industries.
Another challenge is the lack of data on the political and diplomatic implications of trade remedy actions. The database primarily focuses on the economic aspects of these measures, but their political and diplomatic consequences are also significant. Including data on retaliatory measures, diplomatic negotiations, and international disputes could provide a more comprehensive understanding of the broader implications of trade remedy actions.
The Role of the Database in Shaping Future Trade Policies
The Temporary Trade Barriers Database plays a crucial role in shaping future trade policies by providing valuable insights into the causes and consequences of trade remedy actions. The database’s comprehensive records allow policymakers to identify patterns and trends in trade remedy actions, which can inform their policy decisions.
For example, the database’s data on the proliferation of antidumping measures could inform policies aimed at preventing trade wars and promoting fair trade practices. Similarly, the database’s insights into the impact of safeguard measures on global supply chains could inform policies aimed at protecting domestic industries without disrupting international trade.
Furthermore, the database’s detailed records on investigations, targeted products, and affected entities can help policymakers anticipate future trends in trade remedy actions. For instance, a government anticipating increased competition from imported goods could use the database’s data to implement preventive measures to protect its domestic industries.
Insights from Instachronicles
How the Database Provides Unique Insights for Our Readers
Instachronicles is committed to providing our readers with unique insights into global trade dynamics. The Temporary Trade Barriers Database is an invaluable tool for understanding the complex landscape of trade remedy actions and their impact on international trade. Our readers, including business leaders, policymakers, and academics, can leverage the database to make informed decisions and shape future trade policies.
For business leaders, the database offers a strategic advantage by providing detailed information on trade remedy actions that could affect their supply chains and markets. By monitoring the database, businesses can anticipate potential disruptions and adjust their strategies to mitigate risks and seize opportunities. For instance, a company
Conclusion
In wrapping up our exploration of the Temporary Trade Barriers Database managed by the World Bank Group, it’s evident that this repository serves as a critical tool in navigating the complex landscape of global trade. The database meticulously tracks various forms of trade barriers, such as tariffs, quotas, and other restrictions that countries impose on imports or exports, often on a temporary basis. By providing comprehensive and up-to-date information, the database supports policymakers, businesses, and researchers in understanding the intricacies and impacts of these trade policies.
The significance of this resource cannot be overstated, as it aids in fostering transparency and mitigates the risks of trade disputes. It empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions, potentially averting economic downturns and promoting fair trade practices. Looking ahead, as global trade increasingly becomes a focal point of international relations, the role of such databases will be even more pivotal. They will not only help in resolving existing trade conflicts but also in preventing future ones by providing a platform for open and consistent communication between trading nations.
